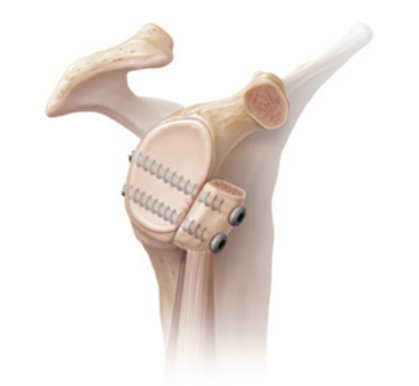
Shoulder instability due to glenoid bone loss (GBL) is a significant concern for athletes and active individuals. Traditional surgical approaches, such as the classic Latarjet procedure, have been widely used to restore stability. However, emerging techniques like distal tibial allograft (DTA) reconstruction are gaining traction for their ability to enhance glenoid concavity. A study conducted by Dr. Okoroha’s colleagues, to compare these two procedures sheds light on their effectiveness in restoring anterior glenohumeral stability.
Study Highlights
Patient Demographics:
Nine human cadaveric specimens, with a mean age of 62.2 years (range, 52-69 years), were used to assess glenoid concavity and anterior stability.
Follow-ups:
Pre- and post-procedure computed tomography (CT) scans were utilized to measure glenoid concavity restoration, along with biomechanical testing to analyze anterior humeral head translation.
Positive Outcomes:
DTA reconstruction demonstrated superior glenoid concavity restoration compared to the Latarjet procedure (BSSR: 0.45 vs 0.35; P < .001). Both techniques provided equivalent reductions in anterior translation when the Latarjet procedure included the conjoint tendon sling effect (5.1 mm vs 4.7 mm; P > .999). However, DTA significantly decreased anterior translation compared to Latarjet without the sling effect (5.1 mm vs 10.3 mm; P = .045).
Conclusion
For patients with glenoid bone loss, both DTA reconstruction and the classic Latarjet procedure provide effective solutions for restoring shoulder stability. The study highlights that DTA produces a more concave reconstruction, potentially offering superior biomechanical benefits. While the Latarjet procedure with the sling effect remains effective, the findings suggest that DTA may be a valuable alternative, especially for those seeking optimal concavity restoration. Surgeons and patients should consider these insights when determining the best surgical approach for long-term shoulder stability.
At Mayo Clinic, located in Minneapolis, Minnesota, we are committed to providing personalized care and innovative treatments to help athletes reach their full potential. To learn more about shoulder instability, arthritis of the shoulder, shoulder labral tears, and shoulder labral repair, schedule a consultation with Dr. Okoroha today. Seeing patients from Minneapolis, St. Paul, Plymouth, Edina, Minnetonka, Rochester, and Minnesota ensures that athletes receive specialized care aimed at maximizing their athletic performance and long-term shoulder health.
To learn more about arthritis of the shoulder and shoulder instability visit: